Is there a more compelling way to understand complex data than through the visual power of a well-crafted graph? Indeed, the ability to translate abstract numbers into easily digestible visual stories is a cornerstone of effective communication, analysis, and decision-making in today's data-driven world.
Graphical representation, at its core, is the art and science of transforming raw data into visual formats like charts, plots, and diagrams. This process extends far beyond mere aesthetics; it's a powerful tool for simplifying intricate datasets, revealing patterns, and communicating insights in a way that resonates with audiences of all backgrounds. The versatility of graphical representation is remarkable. It can be applied across countless fields, from scientific research and financial analysis to journalism and marketing. With just a glance at the graphical representation, a person can make quick and informed decisions.
Consider the application of graphical representation. In the field of finance, line graphs might track stock prices over time, helping analysts identify trends and make investment decisions. In healthcare, histograms could illustrate the distribution of patient ages, assisting doctors in understanding demographics. In marketing, pie charts could display market share, giving businesses insight into the performance of competitors and their own brand.
- Bollyflix In Your Ultimate Guide To Streaming Bollywood Movies
- Whats The Deal With Mmsdosecome A Deep Dive Into This Mysterious Phenomenon
Graphical representations encompass a wide variety of techniques, these techniques are used to clarify, interpret and analyze data by plotting points and drawing line segments, surfaces and other geometric forms or symbols. The purpose of a graph is a rapid visualization of a data set.
Despite its advantages, graphic representation also presents challenges. One common issue is the potential for misrepresentation of data, which can occur if graphics are poorly designed or if the data is manipulated to convey a misleading narrative. Like any other mathematical concept, graphical representation also has some rules you must follow. These rules will help you present the information on a graph effectively.
One of the fundamental principles of graphical representation is its grounding in algebraic principles. Every graph utilizes a coordinate system with two perpendicular axestypically the x-axis (horizontal) and the y-axis (vertical)intersecting at a point called the origin (0,0). The data is then plotted as points on this plane, where each point represents a specific set of values. The position of each point is determined by its coordinates, representing the relationship between variables. The choice of the appropriate graphical method is essential and depends on the type of data and the insights we aim to reveal.
- Unlock The Power Of My Deshico Your Ultimate Guide To Online Learning And Beyond
- Unlocking The Power Of Mmsdose Your Ultimate Guide To Boosting Mobile Marketing
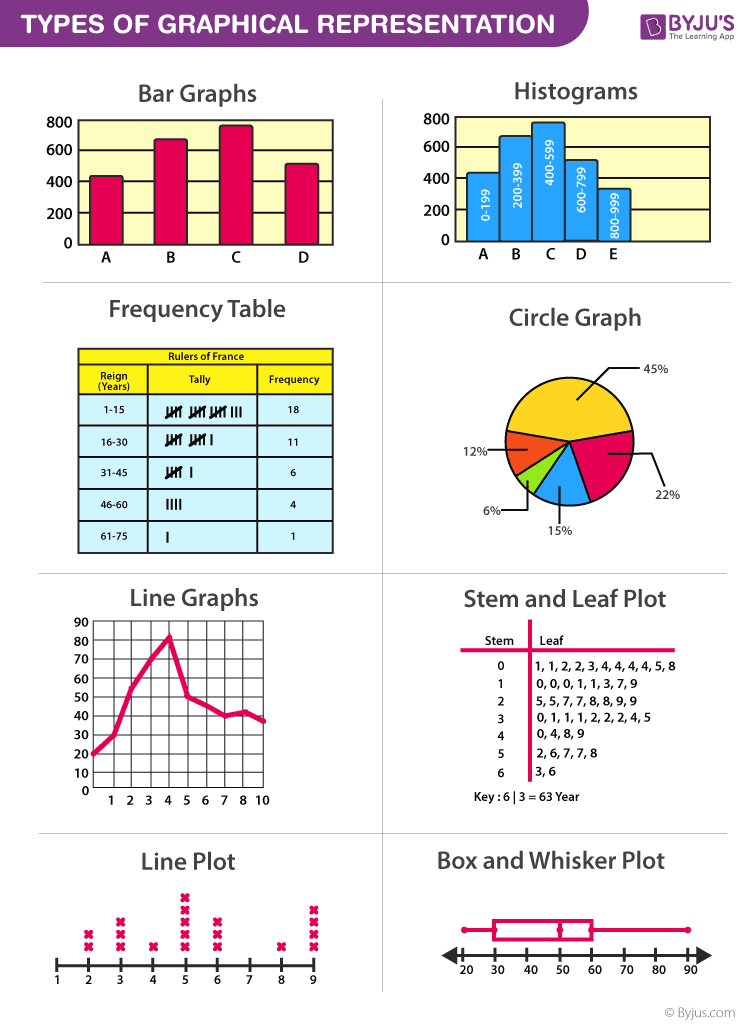
Different types of graphs serve distinct purposes and are best suited for specific types of data. Bar charts are excellent for comparing categories, using rectangular bars to represent data values. Line graphs are ideal for showing trends over time. Histograms provide a visual representation of the frequency distribution of continuous data series using rectangles. Pie charts showcase proportions and percentages of a whole. Scatter plots reveal relationships between two variables. Graphical representation of grouped data can be represented by using histogram, frequency polygon, cumulative frequency curve or ogive ratio diagram/ arithlog graphical representation of ungrouped data can be represented by using 1.line graph.
Data visualization is the process of creating graphical representations of information. This process helps the presenter communicate data in a way thats easy for the viewer to interpret and draw conclusions. Graphical representations are useful tools for visualizing and interpreting data. Learn more about how to read, compare, and find points on line. Creating impactful graphical representations requires careful planning and attention to detail. Here are some tips to help you create effective visuals: Clearly define the message you want to convey with your graph. What insights do you want your audience to gain?
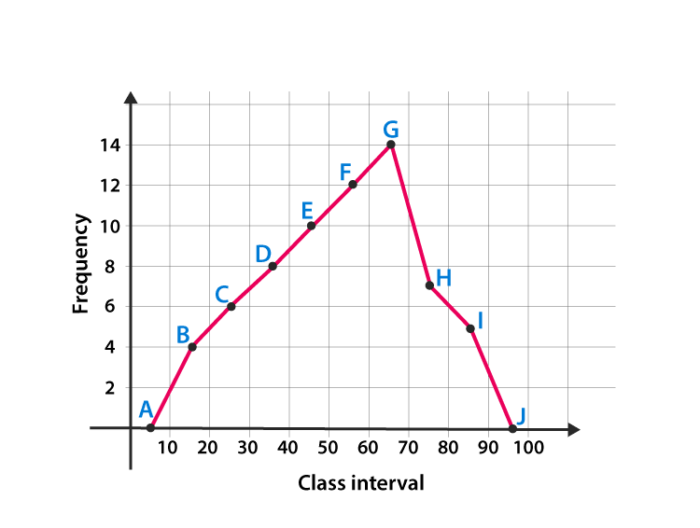
Graphical representations are useful tools for presenting statistical data in a visual format that is easier to understand compared to textual or tabular representations. They translate complex numerical concepts into simple, concrete forms through the use of diagrams, charts, and plots. With just a glance at the graphical representation, a person can make quick and informed decisions. Even when both axes are present and labeled correctly, graphical representations of data can be misleading. This is shown in the set of attendance graphs that follow. In the graph on the left, the scale begins at 0 and goes to 20,000. In this chapter, you will study graphical ways to describe and display your data. You will learn to create, and more importantly, interpret a variety of graph types, and you will learn when to use each type of graph. A statistical graph is a tool that helps you learn about the shape or distribution of a sample or a population. The principles of graphical representation are algebraic.
The selection of a specific graphical format depends on the nature of the data. For instance, bar charts excel at illustrating comparisons between different categories, while line graphs are best for demonstrating changes over time. Histograms are used to display the frequency distribution of continuous data series by using rectangles. Pie charts serve to present proportions and percentages of a whole. Scatter plots are employed to reveal relationships between two variables. The type of graphical representation you choose will be based on the type of data you have.
The importance of graphical representation goes beyond just presentation; it is an indispensable component of modern data practices, bridging the gap between complex data sets and actionable insights. By leveraging visual tools, analysts and data scientists can communicate their findings effectively, fostering a deeper understanding of the data. It serves as an efficient tool for summarizing large amounts of information, enabling the rapid identification of patterns and anomalies that might be hidden in raw data. Furthermore, graphical representation can facilitate forecasting, as it indicates the trend of the data in the past. The principles of graphical representation are algebraic. In a graph, there are two lines known as axis or coordinate axis. They are perpendicular to each other and intersect at o or point of origin.
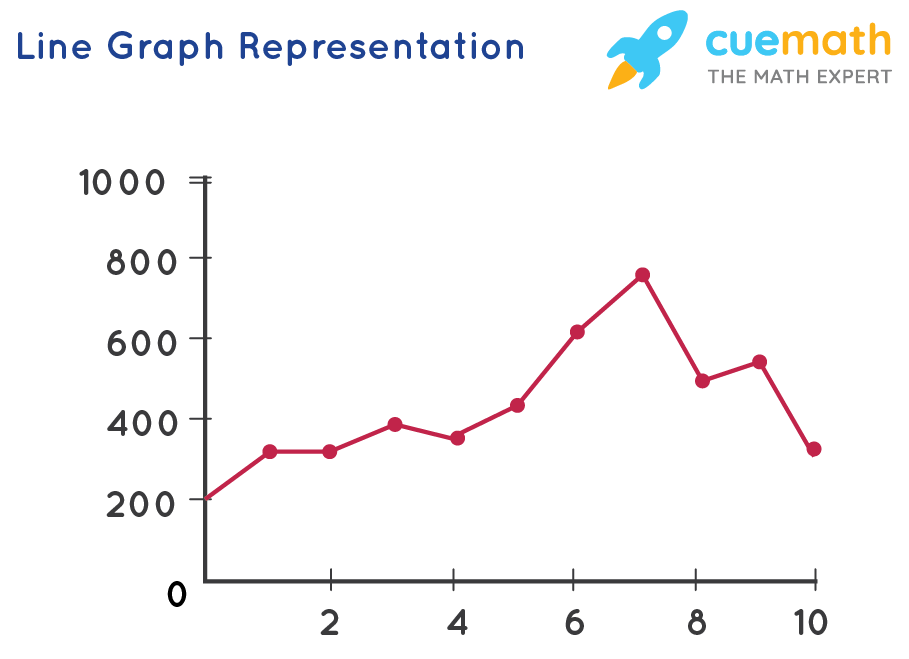
For example, a line graph could track a company's sales revenue over several years, allowing stakeholders to identify trends such as growth, decline, or seasonality. A bar chart might compare the market share of different products, highlighting which ones are most successful. A scatter plot could show the correlation between advertising spend and sales, helping to optimize marketing strategies. These examples highlight the versatility of graphical representation in diverse business contexts.
Graphical methods offer diverse ways to represent data, but some formats are especially common and useful. Bar charts display data with rectangular bars, where each bar represents a category, and the height or length corresponds to its value. Line graphs use lines to connect data points, depicting trends and changes over time. Pie charts use slices of a circle to show proportions of a whole. Scatter plots use dots to show the relationship between two variables. These are just a few of the many types of graphs available, each designed to highlight different aspects of the data.
When creating graphical representations, several rules should be observed. Axes must be clearly labeled with appropriate scales and units. The choice of the right graph type is crucial, depending on the data and the message. Clarity, simplicity, and accuracy are essential. Avoid clutter and ensure the visual elements support the data and insights you aim to convey. Consider your audience and tailor the graph accordingly to ensure it is easily understood and conveys the intended meaning.
Creating effective graphical representations requires careful planning and attention to detail. Consider the following tips: Clearly define the message you want to convey with your graph. What insights do you want your audience to gain? Choose the right graph type for your data. Label axes clearly. Use a clear and concise title. Use appropriate scales. Provide a key or legend if necessary. Avoid clutter. Make sure your graph is accurate and free of misleading information. Consider your audience. Proofread your graph before sharing it.
In an era of Big Data and rapid information processing, the ability to create, interpret, and utilize graphical representations is no longer a specialized skillit is a fundamental requirement for anyone seeking to navigate the complexities of the modern world. From the classroom to the boardroom, in research labs and newsrooms alike, this skill is a core competency.
If you are looking for the best platform to create your own customized charts & diagrams, then Canva's free online graph maker is a great option. You can choose from 20+ chart types & hundreds of templates.
The study of graphical representations is more than just learning to create charts and graphs; it is about cultivating a new way of thinkinga visual literacy that empowers individuals to engage with data on a deeper level. Whether you're a student, a professional, or simply a curious citizen, understanding the art and science of graphical representation is an invaluable asset in today's information age.
- Yesmina Khan The Rising Star In The World Of Entertainment
- Mia Khalifa Telegram The Ultimate Guide To Her Journey And Presence