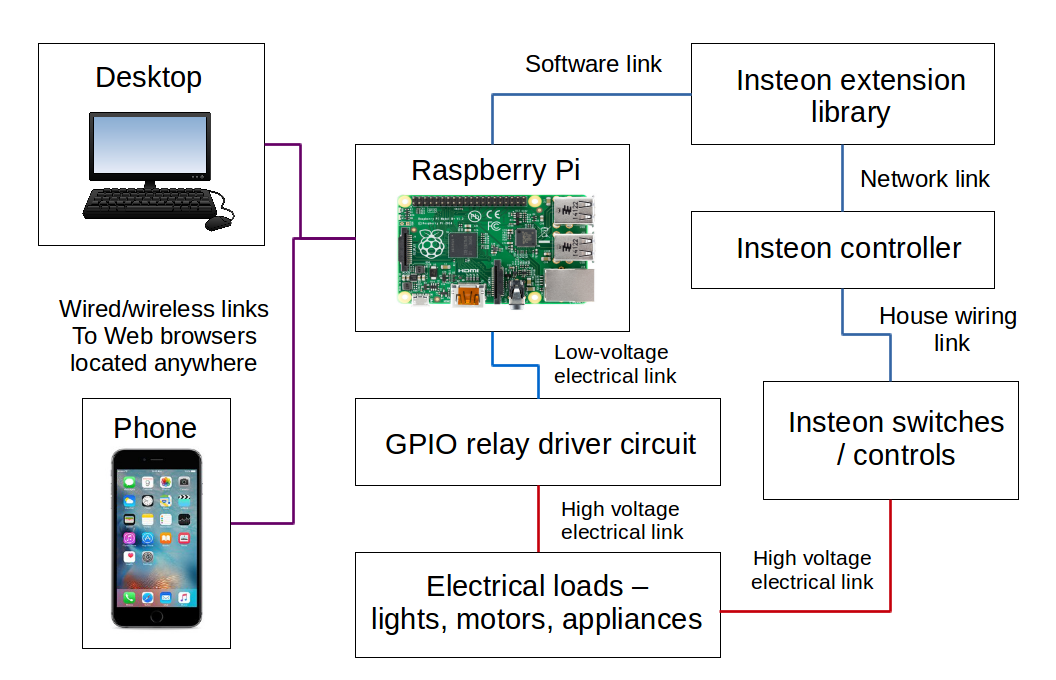
Are you seeking a robust, cost-effective solution for remotely managing and monitoring your devices, even across vast distances? The Raspberry Pi, a pocket-sized computer, presents an incredibly versatile answer, offering a wealth of options for remote access, monitoring, and control that extend far beyond its modest price tag.
The ability to remotely access and manage devices is increasingly crucial in today's interconnected world. Whether you're overseeing a home network, managing a fleet of servers, or simply keeping an eye on your 3D printer, the need to monitor and control devices without being physically present is paramount. The Raspberry Pi, with its compact size, low power consumption, and open-source nature, has emerged as a particularly attractive solution for these challenges. From basic network monitoring to complex industrial control systems, the Raspberry Pi's adaptability makes it a powerful tool for both hobbyists and professionals alike.
This article explores the myriad ways in which a Raspberry Pi can be employed for remote management and monitoring. We'll delve into various methods, from simple ping tests and SSH connections to advanced monitoring software and remote desktop solutions. We'll also explore real-world applications, highlighting how the Raspberry Pi is used in diverse environments, from home automation and environmental monitoring to industrial automation and remote control of equipment. By leveraging the Raspberry Pi's capabilities, you can gain unprecedented control and insight into your devices, no matter where you are.
- Bollyflix Hindi Dubbed Your Ultimate Guide To Streaming Bollywood Movies
- Bollyflixcom Vip Your Ultimate Guide To Streaming Bollywood Movies
| Method | Description | Tools/Software | Use Cases |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ping Monitoring | Simple method to check if the Raspberry Pi is online and reachable. | Ping command (available in most OS) | Basic uptime monitoring, network connectivity checks. |
| SSH (Secure Shell) | Secure remote access to the command line interface. Allows for running commands, managing files, and more. | SSH client (e.g., PuTTY, Terminal), SSH server (installed on the Raspberry Pi) | System administration, software updates, remote troubleshooting. |
| Linux Dash Dashboard | A web-based dashboard for monitoring system resources. | Linux Dash | CPU usage, memory usage, disk space, and network traffic monitoring |
| LibreNMS | A network monitoring system for checking device status and alerting on failures. | LibreNMS | Network device monitoring, performance analysis, and alerts |
| Nagios | A powerful and popular open-source monitoring tool for network devices and services. | Nagios Core, Nagios Plugins | Comprehensive monitoring of servers, services, and network infrastructure. |
| Cockpit | A web-based server management tool for monitoring and managing systems. | Cockpit | System administration, user management, and service monitoring. |
| Remote Desktop Software | Allows remote access to the graphical desktop environment. | VNC, Remmina, XRDP | Remote graphical access, running desktop applications, and file transfer. |
| Mender | An over-the-air (OTA) software update solution for embedded Linux devices, including Raspberry Pi. | Mender client and server | Remote software updates, security patching, and device management. |
| xki.cloud | A platform for managing devices, events, and users from a central dashboard. | xki.cloud | Centralized device management, data visualization, and event monitoring. |
| Atlas IoT | Uses Raspberry Pi for a new monitoring system for various applications. | Atlas IoT software | Water quality monitoring, environmental monitoring, and more. |
| Genmon | Software used to monitor and remotely control a Generac standby generator. | Genmon | Remote control and monitoring of generators. |
| OctoPrint | A web interface for 3D printers, allowing control and monitoring. | OctoPrint | 3D printer control, print job monitoring, and remote management. |
| SolarAssistant | Software to manage and monitor solar power systems. | SolarAssistant | Solar panel system monitoring and management |
One of the most straightforward approaches to remote monitoring is to establish a simple "ping" to the Raspberry Pi. This involves sending a small data packet to the device and waiting for a response. If the Pi responds, it's online and reachable. This is a basic but essential starting point. Further, by combining a public IP address and appropriate port forwarding on your router, the monitoring capabilities can even be extended over the internet, allowing you to check your devices from anywhere in the world. This rudimentary method provides a quick snapshot of the device's availability.
SSH, or Secure Shell, takes remote access a step further. This protocol allows you to securely connect to the Raspberry Pi's command line interface. Once connected, you can execute commands, manage files, and perform various system administration tasks as if you were sitting in front of the device. Common commands like `top`, which displays real-time system resource usage, become invaluable for understanding the Pi's performance. SSH is a cornerstone of remote Raspberry Pi management, offering a powerful and versatile means of control.
Beyond these basic methods, a variety of software solutions are designed specifically for network monitoring. LibreNMS, for example, is a robust network monitoring system that can monitor the status of network devices, create alerts based on failures, and provide in-depth performance metrics. Similarly, Nagios is a well-established and widely-used open-source monitoring tool offering even more comprehensive capabilities. These tools often require a bit more setup but offer far greater control over your monitoring environment. They're particularly useful for monitoring a fleet of devices or for environments where detailed system health information is critical.
- Bollyflixwin The Ultimate Destination For Bollywood Enthusiasts
- Bolliflixcom The Ultimate Destination For Bollywood Enthusiasts
For those seeking a more user-friendly approach, Cockpit provides a web-based interface for server management. This interface allows you to monitor and manage your Raspberry Pi remotely through a web browser. Cockpit simplifies many system administration tasks and provides an easy-to-navigate interface for tasks like user management, service monitoring, and system resource analysis. Furthermore, remote desktop software such as VNC or Remmina gives you graphical access to your Raspberry Pi's desktop environment, allowing you to use applications and manage files just as if you were physically present.
The versatility of the Raspberry Pi extends to specific applications, such as 3D printing and environmental monitoring. OctoPrint is a web interface specifically designed for 3D printers. It allows you to control and monitor print jobs remotely, offering a convenient way to manage your printer from anywhere with an internet connection. Moreover, projects like Atlas IoT use the Raspberry Pi to create powerful environmental monitoring systems. These systems can be customized to monitor parameters such as water quality, temperature, and more, providing valuable data for a variety of applications.
In addition to software-based solutions, the Raspberry Pi is also compatible with various hardware additions to enhance its monitoring capabilities. For instance, to monitor diesel generators remotely, or to gather data from solar power systems, you can use the Raspberry Pi along with converters like the USB to RS485 converter. And to monitor water quality for fish tanks, pools, or hydroponics systems, you can combine your Raspberry Pi with various sensors for a complete remote monitoring system.
The Raspberry Pi's capacity for remote access extends to its ability to be updated remotely. Tools like Mender provide over-the-air (OTA) software update capabilities, enabling you to update software on your Raspberry Pi devices without physical access. This is especially valuable for managing a fleet of remote devices, ensuring that all devices are running the latest software and security patches. This functionality simplifies software maintenance.
Choosing the right method for remote management depends on your needs and the complexity of your environment. Simple needs like basic network monitoring might be satisfied by a simple ping test. For more complex tasks, you might want to consider a web interface dashboard to control your system. Then there are more complex software suites that offer the most detailed information, and these may require a more advanced setup. No matter what your requirements, the Raspberry Pi offers a cost-effective, adaptable solution.
The open-source nature of the Raspberry Pi and the wealth of online resources make it a very accessible platform for both beginners and experienced users. Forums, tutorials, and documentation are readily available, allowing you to learn and adapt the Raspberry Pi to your specific needs. Moreover, the Raspberry Pi's widespread use in various fields has led to the development of a wide array of add-ons, from camera modules and sensors to custom HATs (Hardware Attached on Top), further expanding its versatility.
In short, the Raspberry Pi is an excellent tool for remote management and monitoring. With its small size, low cost, and wide range of features, the Raspberry Pi is suitable for anything from home automation to industrial control systems, allowing anyone to easily connect to their devices, no matter where they are. From basic network monitoring to advanced application control, the Raspberry Pi's versatility makes it a powerful and adaptable solution for today's interconnected world.
- Bollyflix Wwwbollyflixvip Your Ultimate Destination For Bollywood Movies
- Leah Halton Naked A Candid Look At The Controversy And Beyond